Michel van Biezen
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures!
To donate:
http://www.ilectureonline.com/donate
https://www.patreon.com/user?u=3236071
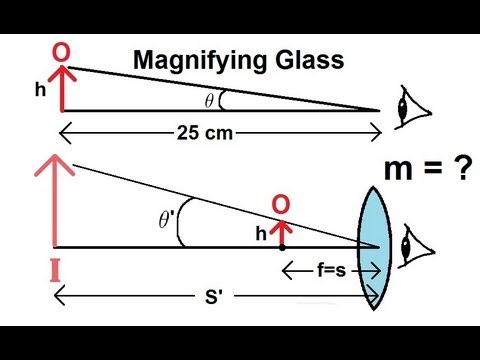
In this video I will have a discussion on the how the magnifying glass works and show you how to find its magnification.
Next video in this series can be seen at:
https://youtu.be/OG4WfWJuA2k
Source



is it just me or he sounds like gru from despicable me anyways great lectures
Your videos are very helpful, Sir. Thank you so much
I didn't understand why we used m = θ'/θ . I know the approximations. That's not where I'm confused. I haven't seen m = θ'/θ in any of your videos and I wonder the derivation of this equation and how we use such a proportion. I think I didn't understand the angular size and what it means.
if f be the focal length of the objective and f1 that of the eye piece then magnifying power is given by
For the sake of curiosity ! why did you choose 25 cm the distance to the object ?
Sir, assuming that magnification is the ratio between the height of those 2 figures, you can't express it by teta' / teta.
Why did you do that?
Thank you so much, sir. Your video made me clear of what I was confused.
Your vids are a blessing, thank you!
Sir why do we take angel to be very small so that its tangent is same as it is
i have a question. i thought, in the case of convex lens, as the object is moved from the focus towards the lens, the size of the virtual image keeps on decreasing, the highest magnification being when the object is just near the focus, the lowest when the object is just near the lens. then in this example, how does the magnification increase when the object is moved away from the focus?
Thanks! Nice video!
It would be great if you give us tutorial how head up display (HUD) works.
Pls answer
What is the magnifying power of this magnifying glass if we vary the object distance …. does it changes if the focal length is fixed?
Great explanation ! Thanks , it was very helpful.
A lens of focal length 20 cm has an object of area 8.0 cm2 placed 100 cm in front of it. The area of the image is
Hi there I love the this video it has helped me to have a better understanding in this topic. BUT..
i have a confusion, isn't lens the formula (1/F)=(1/V)-(1/U).
you seem to have done this (1/F)=(1/V)+(1/U)
where U=S & V=S1
please correct me if i am wrong.
thank you
why f=s?
Is it because to view an object clearly or to be in focus,
distance of object has to be equal to focal length?
Um, I dot quiet understand on the second part of the video your said we will look through a strained vision , when why we still assume s' is still 25? since N=25 is relax vision
Thank you Sir for your lectures, your methods are very easy to understand yet comprehensive. can u please explain the significance of the equation on the top right ( the one that goes like this: 1/f= 1/s + 1/s') please.
thanks nigga
That was so helpful!! Thank you 🙂
Hi, first of all, thanks for the video! Second. I'd like to ask why it is that you can assume for small angles that tan theta = +/- theta? Looks like I missed out on something there
hello. can you explain why the magnification of a magnifying glass is f/25. I dont understand why theres a 25 at the bottom. couldn't the image be 30 cm away and the equation would be f/30? it just seems like its always going to be f/25 the way it was said in the video. thank you.
hi, i wasnt looking for all these names and numbers- can you do a video that explains how a magnifying glass actually makes the image look bigger…the object stays the same no matter how you look at it but a magnifying glass makes the image look bigger and i dont understand how thats possible- thanks
You sound like a Brooklyn-grown Steve Jobs! Haha 🙂 Thanks so much for your videos 😀
Thanks for the comment. I am glad it helped.
Thank you so much! Amazing video, helped me a lot.