Latif Shaik
20220929 115735
SECONDARY STORAGE DEVICES
Magnetic Storage Devices
Hard disk
Floppy disk
Tape drive
Zip drive
Optical Storage Devices
Compact Disc (CD)
Digital Versatile Disc (DVD)
Blue Ray Disc (BRD)
—————————————————
– Store Operating System, Application, Data- music, video, documents
Internal HDD PATA/SATA
SSD (Solid State Devices) – NVMe – M.2 , SATA
To store data externally – USB Pendrive, USB External HDD
Hard Disk
Uses Magnetic Media for Storing Data
Non-Volatile Permanent Storage Device
Mass Storage Device
Interfaces Used
IDE / EIDE –PATA
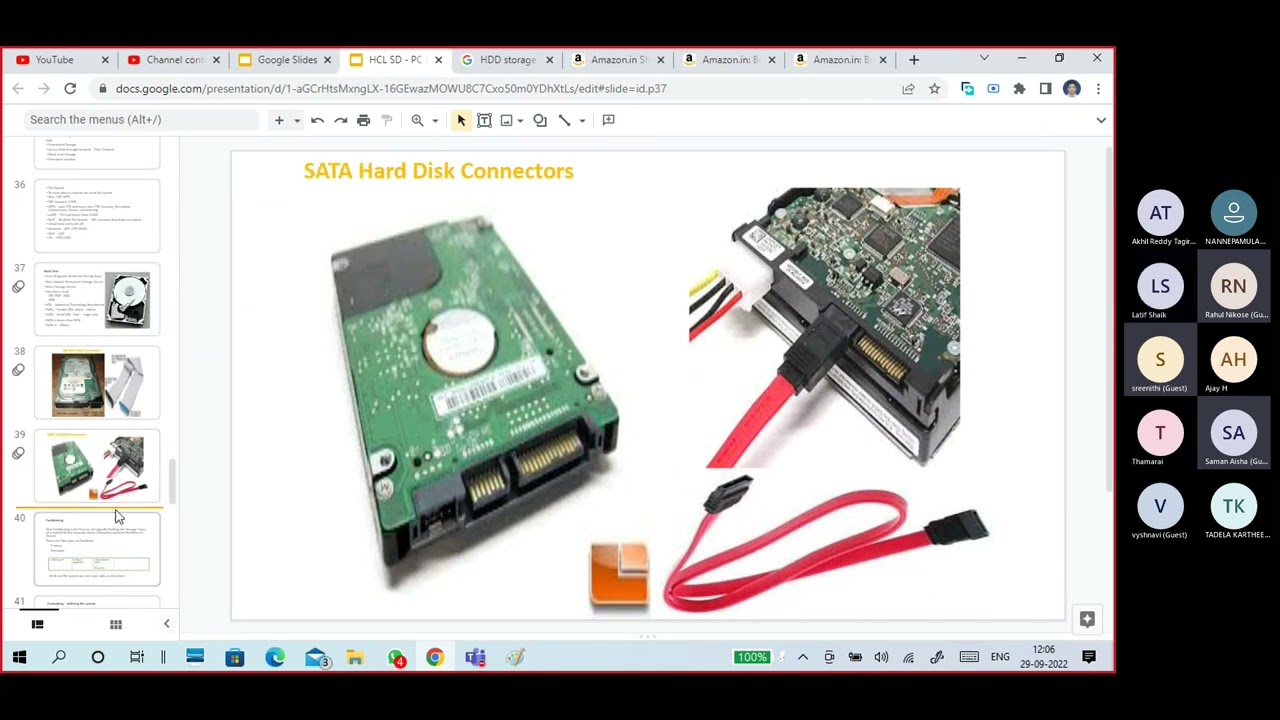
SATA
ATA – Advanced Technology Attachment
PATA – Parallel ATA -40pin – ribbon
SATA – Serial ATA 7pin – single wire
SATA is faster than PATA
SATA III – 6Gbps
Partitioning
Disk Partitioning is the Process of Logically Dividing the Storage Space of a Hard Disk into Separate Areas Commonly called as Partitions or Drivers
There are Two types of Partitions
Primary
Extended
MBR and GPT
When a fresh/new disk drive connected system ask for initialize as MBR type or GPT type
Partition style/Type – MBR or GPT
When we install OS in fresh PC/System – OS and MotherBoard are BIOS firmware – Disk initialize as MBR
MotherBoard – UEFI firmware and OS is latest (uefi support) – Disk initialize as GPT
MBR: Master Boot Record
4 Primary partitions
3 Primary partitions and 1 extended partitions
1 extended –multiple no of logical drives
Partition Size support – upto 2TB
GPT:GUID Partition Table
128 Primary partitions
No extended- no logical
Partition Size : more than 2TB, Upto 18EB
File System
To store data in a device we need file system
Win : FAT, NTFS
FAT: Supports 32GB
NTFS – upto 2TB and more than 2TB, Security, Encryption, Compression, Quota, and Indexing
exFAT – SD Card (more than 32GB)
ReFS – Resilient File System – CRC prevents data from corruption
Linux/Unix: ext3,ext4,xfs
Network – NFS, CIFS (SMB)
DVD – UDF
CD – HSFS,CDFS
SSD – Solid State Drive
-NAND memory
-data stores in chips
-HDD data stores in Platter
-Non volatile
-light weight – carry easily
-easy to transport
-less power consumption
-small size
-high speed -read and write , transmission
-Suitable for Operating and Application
-Not suitable for storing data – we can store but SSD is costly
-costly
-250GB SSD – 1TB HDD
SSD
NAND SATA SSD
-connecting to SATA interface on MB
-Read and Write speeds up to 540MB/s and 500MB/s
NAND NVMe M.2 SSD
-faster than SATA SSD
-costly
-Inserting into motherboard like RAM or CPU
-reads or writes up to 2400MB/s – 1900MB/s